Problem Statement
There is a frog 🐸 on the 1st step of an N stairs long staircase. The frog wants to reach the Nth stair. HEIGHT[i] is the height of the (i+1)th stair.
If Frog 🐸 jumps from ith to jth stair, the energy lost in the jump is given by absolute value of ( HEIGHT[i-1] - HEIGHT[j-1]). If the Frog is on ith staircase, he can jump either to (i+1)th stair or to (i+2)th stair. Your task is to find the minimum total energy used by the frog to reach from 1st stair to Nth stair.
Example
If the given ‘HEIGHT’ array is [10,20,30,10], the answer 20 as the frog can jump from 1st stair to 2nd stair (|20-10| = 10 energy lost) and then a jump from 2nd stair to last stair (|10-20| = 10 energy lost). So, the total energy lost is 20.
Sample Input 1:
2 4 10 20 30 10 3 10 50 10
Sample Output 1:
20 0
Explanation of sample input 1:
For the first test case, The frog can jump from 1st stair to 2nd stair (|20-10| = 10 energy lost). Then a jump from the 2nd stair to the last stair (|10-20| = 10 energy lost). So, the total energy lost is 20 which is the minimum. Hence, the answer is 20.
For the second test case: The frog can jump from 1st stair to 3rd stair (|10-10| = 0 energy lost). So, the total energy lost is 0 which is the minimum. Hence, the answer is 0.
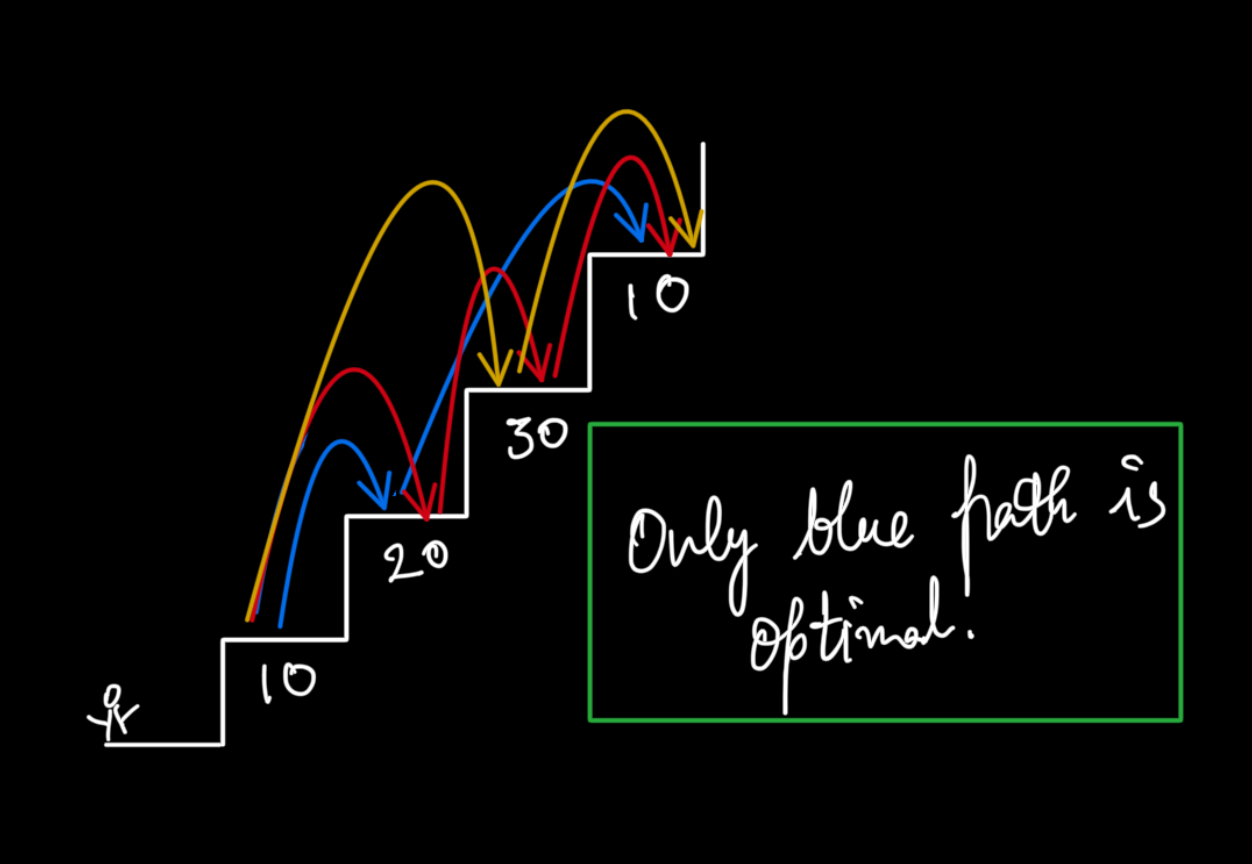
Solution:
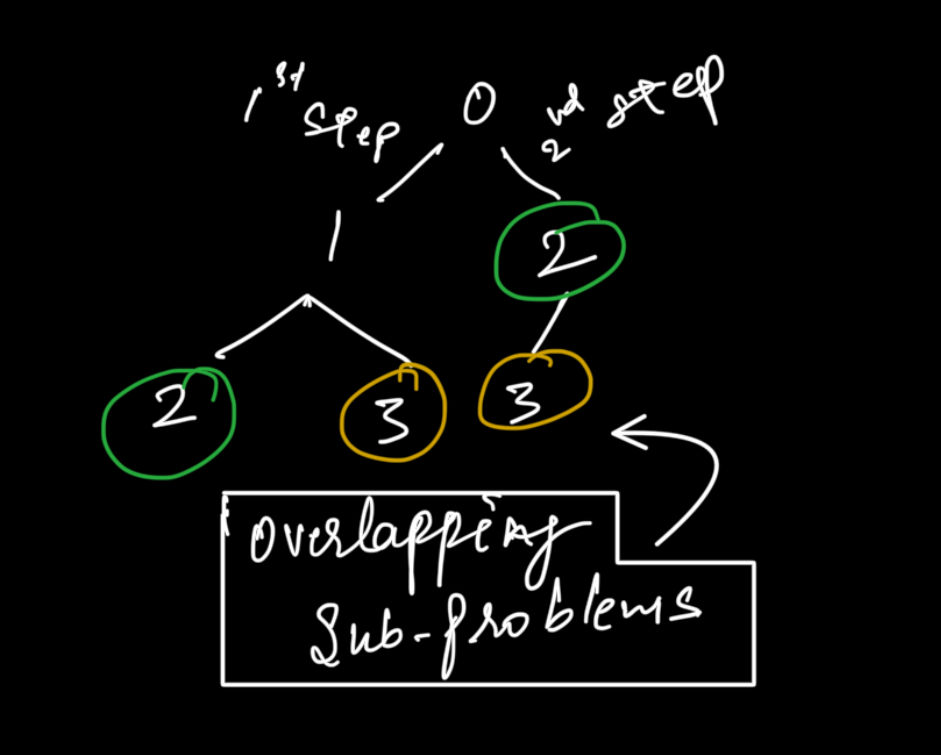
- Memoized recursive solution: (TOP DOWN)
- SC = O(N) + O(N) [memo + stack space]
- TC = O(N)
public class Solution {
public static int func(int idx, int[] heights, int[] memo){
if(idx == heights.length - 1){
return 0;
}
if(idx == heights.length - 2){
return Math.abs(heights[idx] - heights[idx + 1]);
}
if(memo[idx] != -1){
return memo[idx];
}
int jumpOne = Math.abs(heights[idx + 1] - heights[idx]) + func(idx + 1, heights, memo);
int jumpTwo = Math.abs(heights[idx + 2] - heights[idx]) + func(idx + 2, heights, memo);
return memo[idx] = Math.min(jumpOne, jumpTwo);
}
public static int frogJump(int n, int[] heights){
int[] memo = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(memo, -1);
return func(0, heights, memo);
}
}- Tabulation solution:(BOTTOM UP)
- SC = O(N)
- TC = O(N)
public class Solution {
public static int func(int[] heights, int[] dp){
int n = heights.length;
//Base cases
dp[n - 1] = 0;
dp[n - 2] = Math.abs(heights[n - 2] - heights[n - 1]);
// start filling from right to left
for(int i = n - 3; i >= 0; i--){
int jumpOne = dp[i + 1] + Math.abs(heights[i + 1] - heights[i]);
int jumpTwo = dp[i + 2] + Math.abs(heights[i + 2] - heights[i]);
dp[i] = Math.min(jumpOne, jumpTwo);
}
return dp[0];
}
public static int frogJump(int n, int[] heights){
int[] dp = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
return func(heights, dp);
}
}- Space optimization
- SC = O(1)
- TC = O(N)
public class Solution {
public static int frogJump(int n, int[] heights){
//Base cases
int last = 0;//dp[n-1]
int secondLast = Math.abs(heights[n - 2] - heights[n - 1]); //dp[n-2]
int curr = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// start filling from right to left
for(int i = n - 3; i >= 0; i--){
int jumpOne = secondLast + Math.abs(heights[i + 1] - heights[i]);
int jumpTwo = last + Math.abs(heights[i + 2] - heights[i]);
curr = Math.min(jumpOne, jumpTwo);
last = secondLast;
secondLast = curr;
}
return curr;
}
}