Question:
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Example 1:
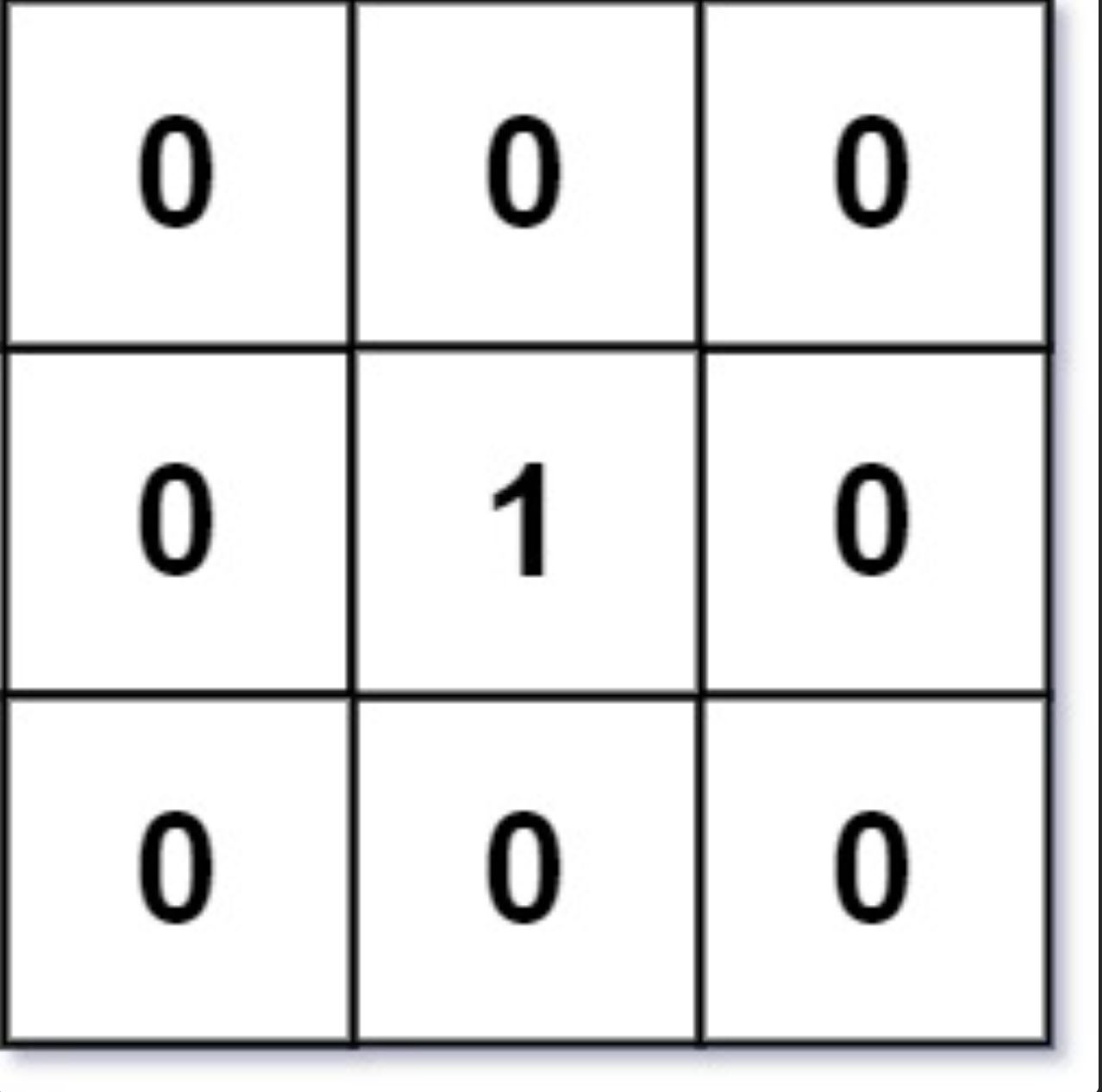
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]] Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Example 2:
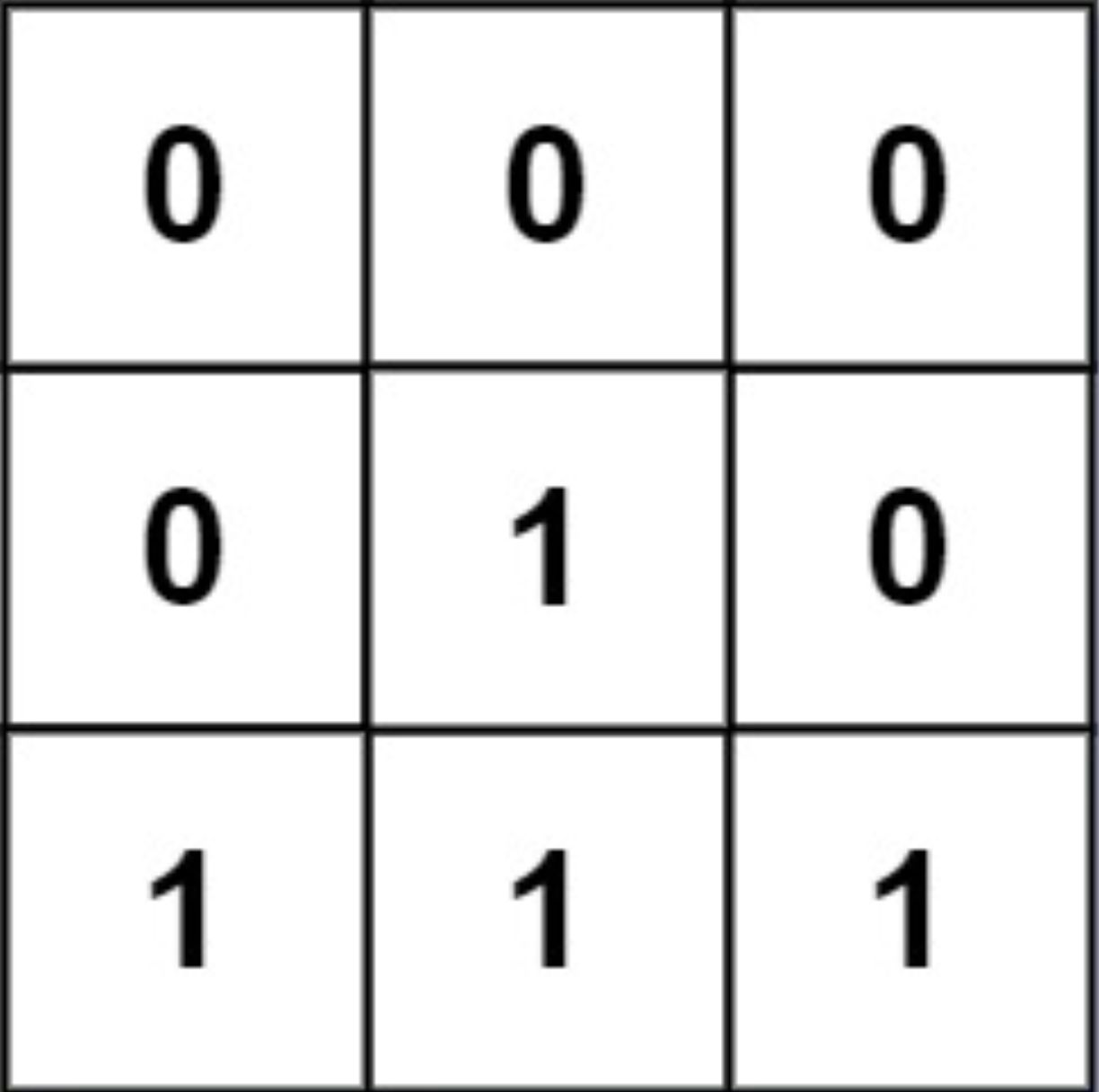
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]] Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^41 <= m * n <= 10^4mat[i][j]is either0or1.- There is at least one
0inmat.
Solution:
- Hum 0 se nearest 1’s pe jaate hai from BFS. Also, hum steps leke chalte hai apne saath, so as soon as we encounter 1 we update it’s distance from the nearest 0 by assigning it currStep + 1;
- The BFS starts from the cells with value 0 and expands to their neighboring cells.
- We initialize the queue with the cells that have a value of 0.
- These cells serve as the starting points for the BFS traversal.
- The distance of cells with value 0 is already known to be 0, so we mark them as visited and enqueue them with a step value of 0.
- The
visitedarray serves two purposes:- Avoiding revisiting cells: It prevents processing the same cell multiple times and avoids infinite loops in case of cycles.
- Ensuring correct distance updates: It guarantees that each cell gets assigned the shortest distance to its nearest 0 cell by skipping the visited cells.
- IF it’s visited means that
1is already assigned the shortest possible path.
- If a neighboring cell has a value of 1 and hasn’t been visited before, we update its distance by adding 1 to the current step value and enqueue it for further exploration.
- The BFS starts from the cells with value 0 and expands to their neighboring cells, gradually updating the distances as it explores further.
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int[][] distances = new int[n][m];
// Find all cells with value 1 and add them to the queue
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
q.offer(new int[] { i, j , 0}); //coordinates (i, j) and current step.
distances[i][j] = 0;
visited[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
// BFS traversal to update distances
int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = q.poll();
int currRow = cell[0];
int currCol = cell[1];
int step = cell[2];
for(int[] direction: directions){
int newRow = currRow + direction[0];
int newCol = currCol + direction[1];
//If it's visited means that `1` is already assigned the shortest possible path.
if(newRow >= 0 && newRow < n &&
newCol >= 0 && newCol < m &&
!visited[newRow][newCol]
){
distances[newRow][newCol] = step + 1; //step + (up, down, left, right)
visited[newRow][newCol] = true;
q.offer(new int[]{newRow, newCol, step + 1});
}
}
}
return distances;
}
}