Problem Statement:
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the diameter of the tree.
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Example 1:
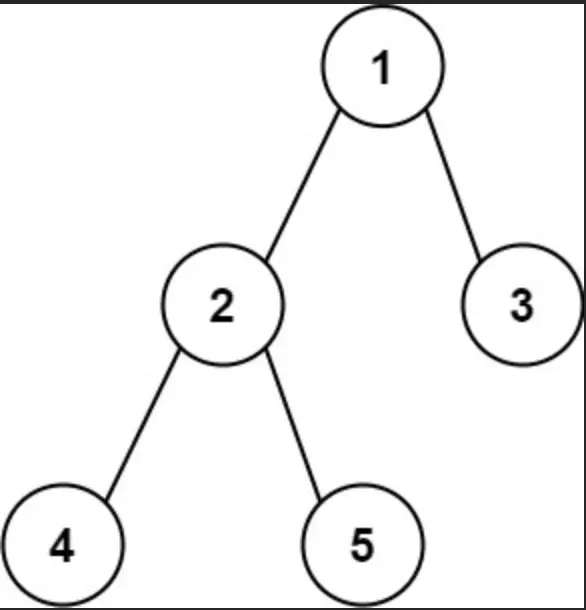
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 3 Explanation: 3 is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
Example 2: Input: root = [1,2] Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution:
Inefficient way (Two Recursive calls o(N^2))
class Solution {
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int lh = 0;
if(root.left != null){
lh = height(root.left);
// System.out.println("lh: " + lh);
}
int rh = 0;
if(root.right != null){
rh = height(root.right);
// System.out.println("rh: " + rh);
}
int curr = lh + rh;
int left = diameterOfBinaryTree(root.left);
int right = diameterOfBinaryTree(root.right);
return Math.max(curr, Math.max(left, right));
}
int height(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0; //-1 for edges and 0 for nodes.
}
int leftHeight = height(root.left);
int rightHeight = height(root.right);
return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
}efficient way:
We calculated height and diameter without needing the height recursive call. O(n)
class Solution {
class TreeInfo{
int height;
int diameter;
TreeInfo(int height, int diameter){
this.height = height;
this.diameter = diameter;
}
}
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
return diameterAndHeight(root).diameter;
}
public TreeInfo diameterAndHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return new TreeInfo(0, 0);
}
TreeInfo left = diameterAndHeight(root.left);
TreeInfo right = diameterAndHeight(root.right);
int currHeight = 1 + Math.max(left.height, right.height);
int currDiameter = Math.max(left.height + right.height, Math.max(left.diameter, right.diameter));
return new TreeInfo(currHeight, currDiameter);
}
}