Types of Binary Trees:
- Full Binary Tree:
- Every node in a full binary tree has either 0 or 2 children.
- There are no nodes with only one child.

- Perfect Binary Tree:
- A perfect binary tree is a full binary tree in which all leaf nodes are at the same level.
- The number of nodes at each level is maximized, and the tree is balanced.
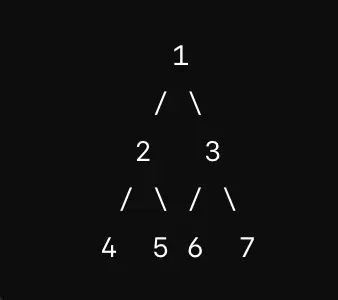
- Complete Binary Tree:
- A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which all levels, except possibly the last level, are completely filled.
- If the last level is not complete, the nodes are filled from left to right.

- Balanced Binary Tree:
- A balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the heights of the left and right subtrees of any node differ by at most one.
- Examples of balanced binary trees include AVL trees and Red-Black trees.
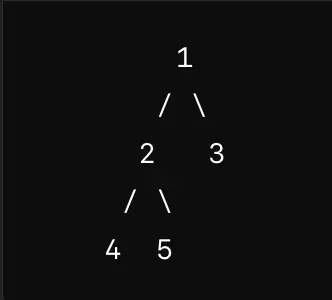
- Binary Search Tree (BST):
- A binary search tree is a binary tree with the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- The left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.

- A binary search tree is a binary tree with the following properties:
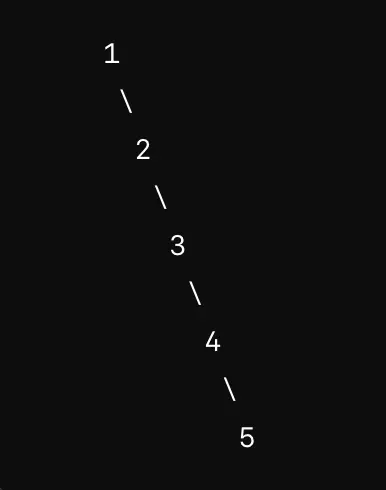
- Degenerate (or Pathological or Skewed) Tree:
- Each parent node has only one child, making it essentially a linked list.
Basic Binary Tree Class :
public class BinaryTree {
class TreeNode {
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
TreeNode root;
BinaryTree(int value) {
root = new TreeNode(value);
}
BinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
// Method to insert node manually
void insertLeft(TreeNode parent, int value) {
if (parent == null) {
System.out.println("The parent node is null. Can't insert.");
return;
}
if (parent.left != null) {
System.out.println("The left child already exists. Can't insert.");
return;
}
parent.left = new TreeNode(value);
}
void insertRight(TreeNode parent, int value) {
if (parent == null) {
System.out.println("The parent node is null. Can't insert.");
return;
}
if (parent.right != null) {
System.out.println("The right child already exists. Can't insert.");
return;
}
parent.right = new TreeNode(value);
}
// ********************* Traversals *********************
//left, root(In), right
void inorder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null){
return;
}
inorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
inorder(node.right);
}
//root(pre), left, Right
void preorder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null){
return;
}
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
//left, right, root(post)
void postorder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null){
return;
}
postorder(node.left);
postorder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
}
void levelOrder(TreeNode node){
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(node);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
TreeNode currNode = q.poll();
System.out.print(currNode.value + " ");
if(currNode.left != null)
q.add(currNode.left);
if(currNode.right != null)
q.add(currNode.right);
}
}
// ********************* Size, Sum, Max, Height *********************
int size(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftSize = size(root.left);
int rightSize = size(root.right);
return 1 + leftSize + rightSize;
}
int sum(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftSum = sum(root.left);
int rightSum = sum(root.right);
return root.value + leftSum + rightSum;
}
int max(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
int leftMax = max(root.left);
int rightMax = max(root.right);
return Math.max(root.value, Math.max(leftMax, rightMax));
}
int height(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return -1; //-1 for edges and 0 for nodes.
}
int leftHeight = height(root.left);
int rightHeight = height(root.right);
return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftT = minDepth(root.left);
int rightT = minDepth(root.right);
if(root.left == null){
return 1 + rightT;
}
if(root.right == null){
return 1 + leftT;
}
return 1 + Math.min(leftT, rightT);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(1); // Root node
tree.insertLeft(tree.root, 2); // Insert 2 as left child of root
tree.insertRight(tree.root, 3); // Insert 3 as right child of root
tree.insertLeft(tree.root.left, 4); // Insert 4 as left child of node 2
tree.insertRight(tree.root.left, 5); // Insert 5 as right child of node 2
tree.insertLeft(tree.root.right, 6); // Insert 6 as left child of node 3
tree.insertRight(tree.root.right, 7);// Insert 7 as right child of node 3
tree.insertLeft(tree.root.left.left, 8);// Insert 7 as right child of node 3
System.out.println("Inorder traversal:");
tree.inorder(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nPreorder traversal:");
tree.preorder(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal:");
tree.postorder(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nLevelOrder traversal:");
tree.levelOrder(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nSize of BT: " + tree.size(tree.root));
System.out.println("\nSum of BT: " + tree.sum(tree.root));
System.out.println("\nMax of BT: " + tree.max(tree.root));
System.out.println("\nHeight of BT: " + tree.height(tree.root));
}
}